⼤気下で安定なpドープポリマーがMacromoleculesに掲載されました。
“Employment of Alkoxy Sidechains in Semicrystalline Semiconducting Polymers for Ambient-Stable p-Doped Conjugated Polymers”
T. Kurosawa, Y. Yamashita, Y. Kobayashi, C. P. Yu, S. Kumagai, T. Mikie, I. Osaka, S. Watanabe, J. Takeya, and T. Okamoto*,
Abstract
Electrical properties arising from doped conducting polymers offer various applications in organic electronics. Recently, sequential chemical doping of semiconducting polymers has attracted attention owing to its capability of being a full solution process, controllable doping level, high electrical properties, and obtaining crystalline conducting polymers. Although the sequentially doped conducting polymers are promising for high electrical conductivities and solid-state physics studies, they show issues of ambient stability due to competitive dedoping. Taking redox reactions with adsorbed water molecules into account as the major dedoping mechanism in p-doped conducting polymers, the fine-tuning of energy levels is a way to improve the ambient stability. In this work, we synthesized two poly(2,5-bis(thiophene-2-yl)thieno[3,2-b]thiophene) regioisomers functionalized with alkoxy side chains to lower the ionization potential by the electron-donating alkoxy groups. After sequential p-doping, the two isomers demonstrated high crystallinities and electrical conductivities on the order of 1 × 102 S cm–1 in air. In addition, the p-doped alkoxy isomers exhibited ionization potentials smaller than the alkyl analogue by ∼0.1 eV, which led to a competition with the redox potential of water. As a result, the stability was remarkably improved, particularly under a high-humidity condition. Therefore, the alkoxy sidechains are promising as a molecular design strategy for conducting polymers with excellent ambient stability.
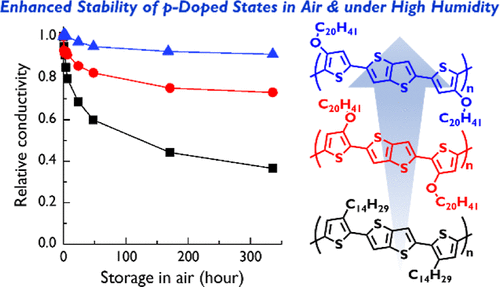
Macromolecules, 57, 328–338 (2024). [DOI:10.1021/acs.macromol.3c00211]